
My Services
Website Development
Custom HTML Sites & WordPress – Business, portfolio, blog, and store websites
Google Services
Analytics, Search Console, Tag Manager – Full setup with tracking and reporting
SEO Optimization
On-page, Technical & Blog SEO – Keyword research, meta tags & sitemap.
Graphic Design
Professional logos, flyers, social media visuals, and invoice designs that strengthen your brand identity.
Blog Setup & Writing
SEO-friendly blog setup and article writing services that attract traffic and keep readers engaged.
Social Media
Set up and integrate business social media accounts seamlessly with your website.
Portfolio
Welcome to Gadget Crunchie, visit Portfolio page to see my completed projects.
Completed Projects
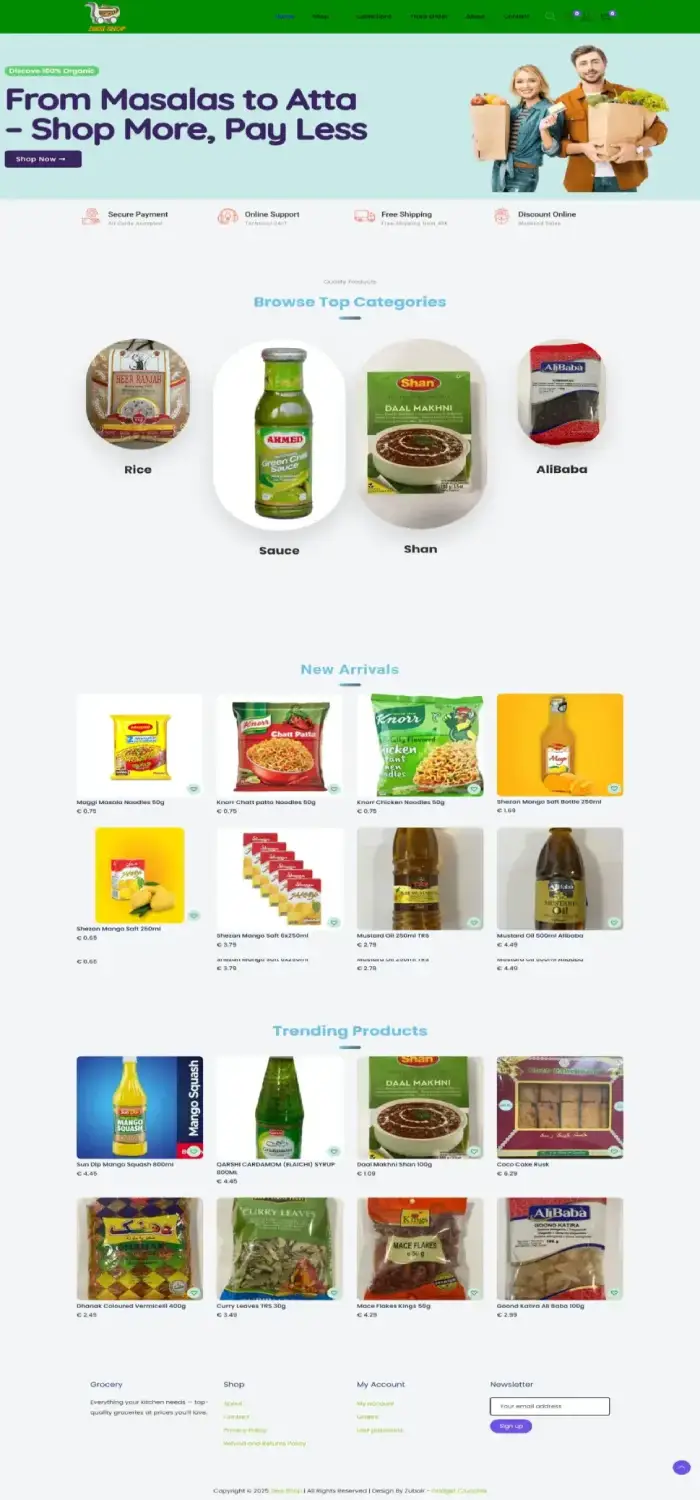
Desi Grocery Store
Germany Grocery Store Website
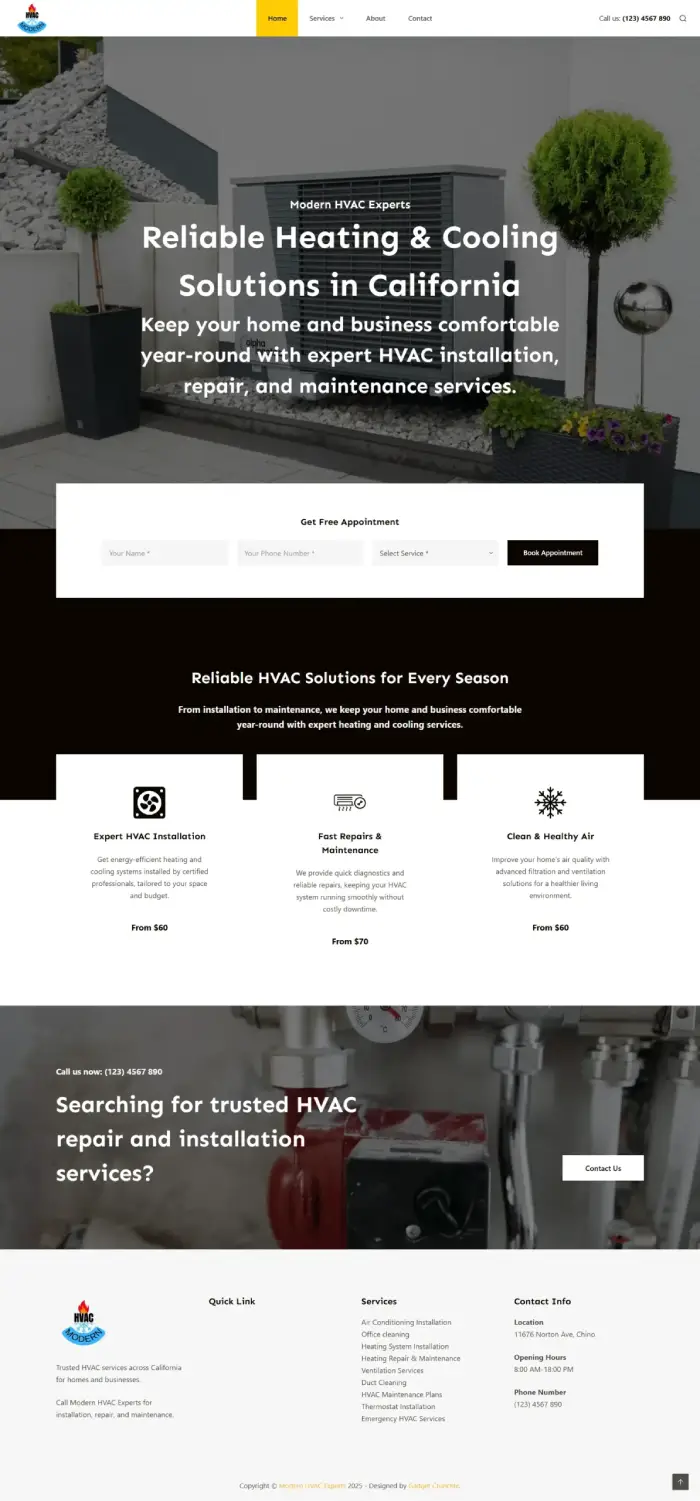
Modern HVAC Experts California USA
American HVAC Website
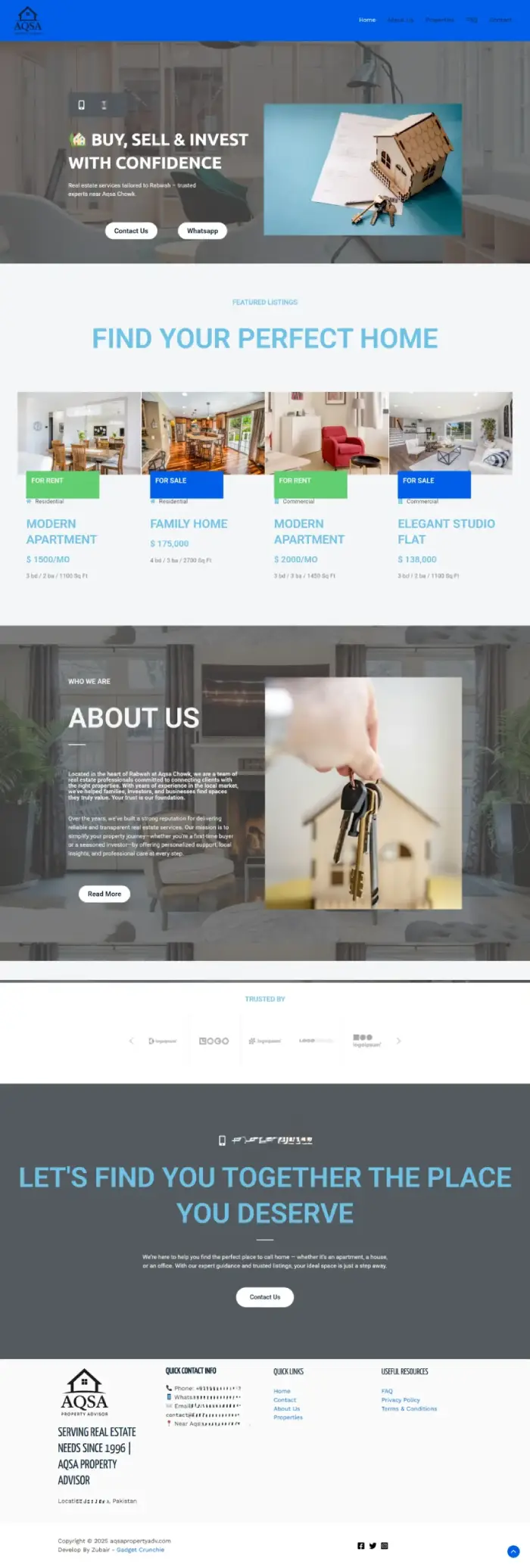
Aqsa Property Adv
Real State Property Website
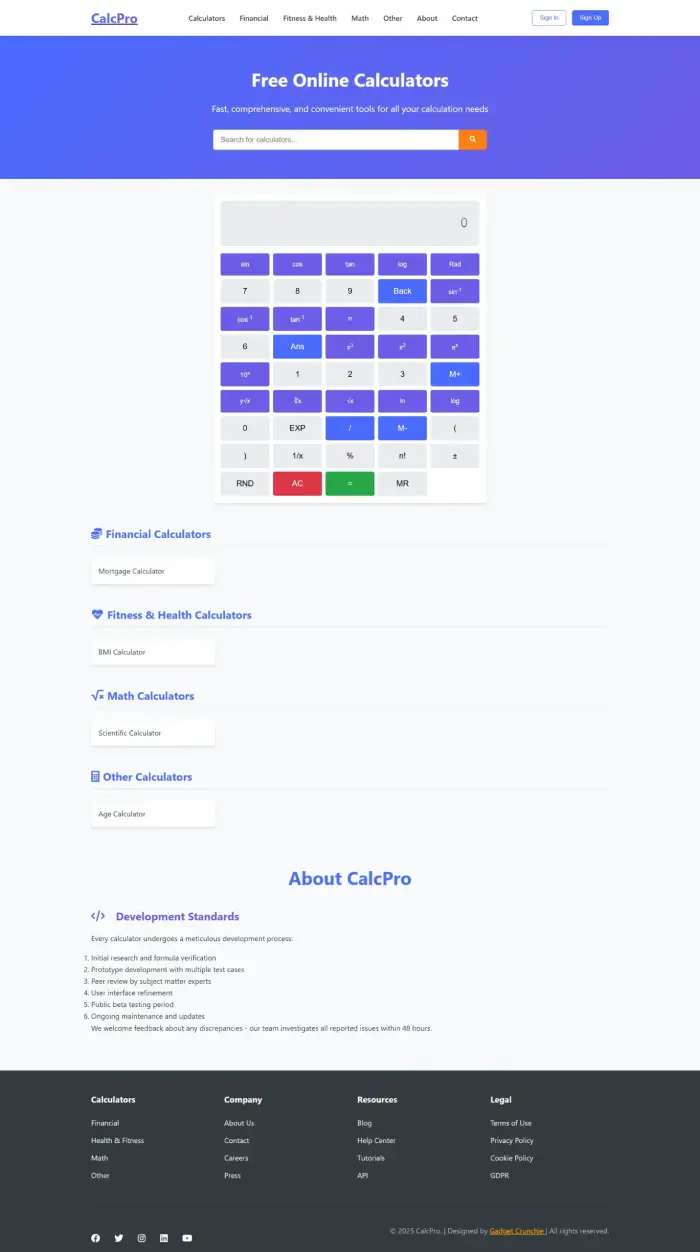
calculators-website
HTML + CSS + Javascript, Clean UI

localhost-VizionSite
Sample site
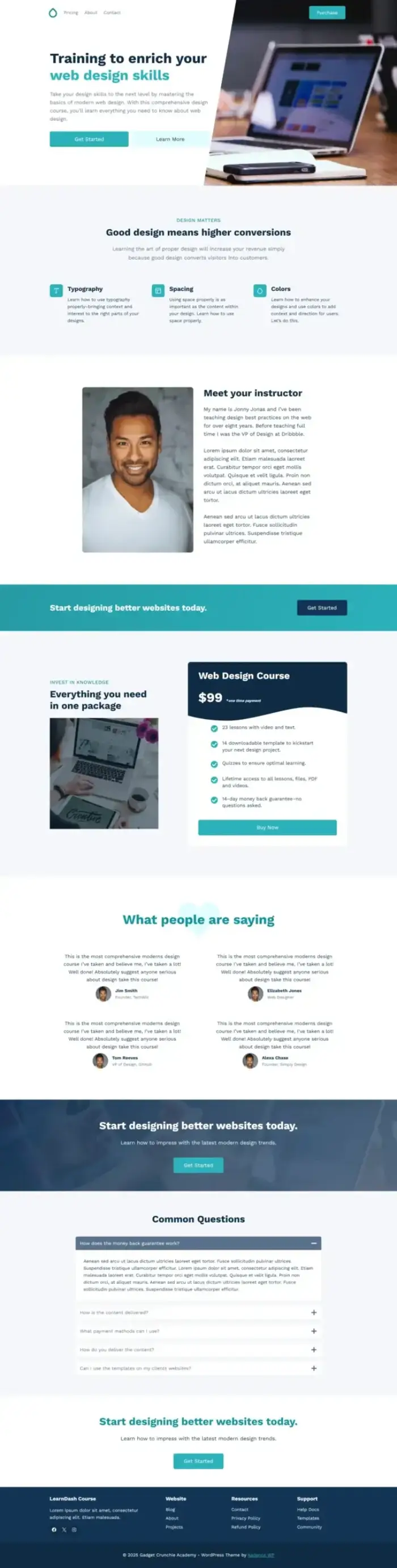
Academy Website
WordPress LMS with blog
visit privacy policy page
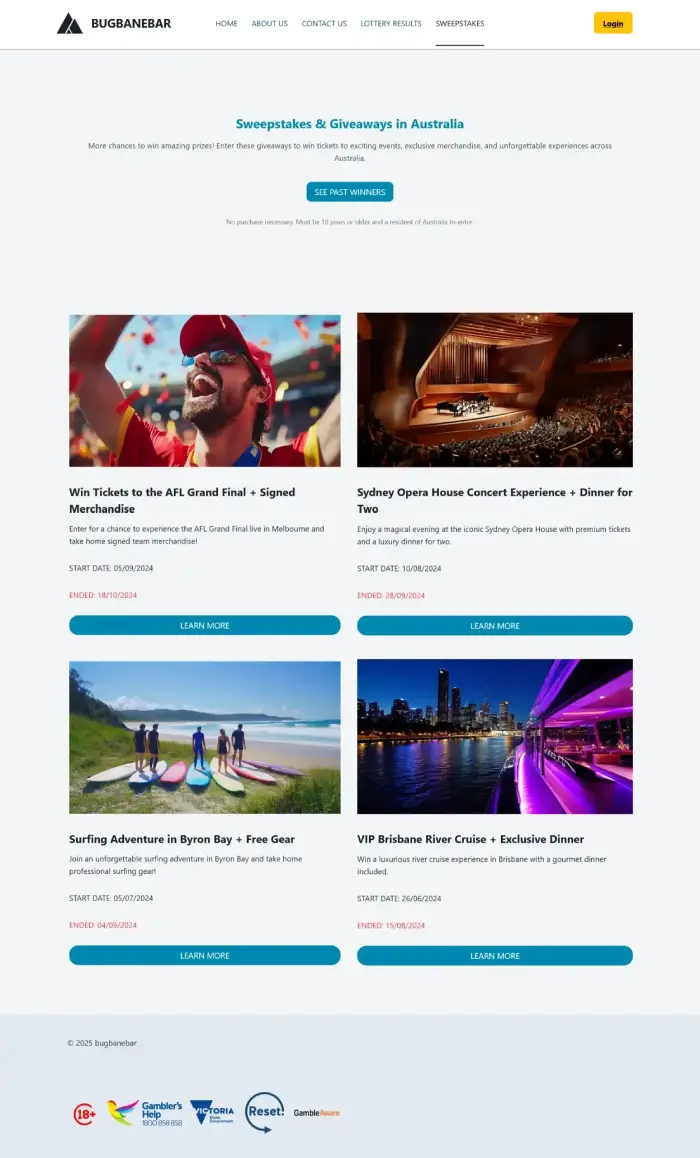
Sweepstakes Site
Lottery entries and blog

Lottery Result Site
HTML + CSS, Clean UI
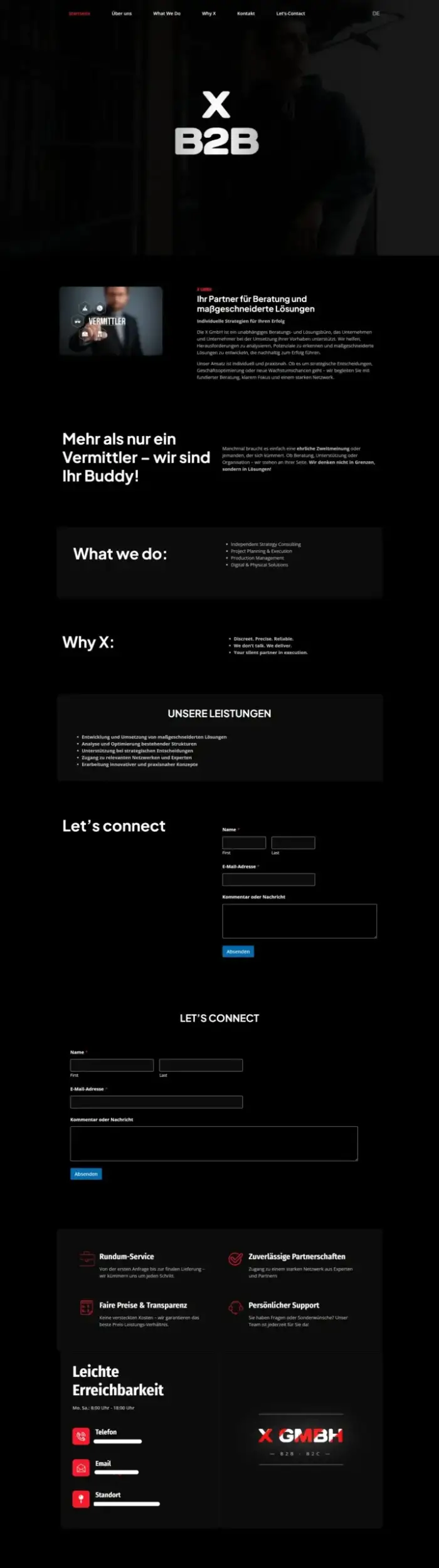
GMBH CH Site
Germany Site Dutch Language
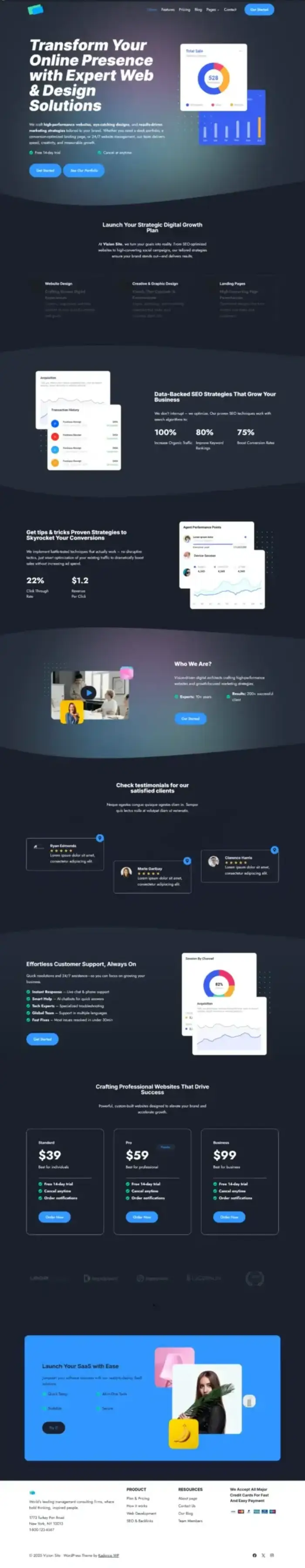
Vizion Site
Local Host Design

BugbanebarSite
Local Host Design
Popular Blog Posts
From The Archives (Old Posts)
Latest Blog Posts
Testimonials

Gadget Crunchie built a clean and professional WooCommerce store for my gadget business. Sales improved within weeks!
— Ali Raza, Online Gadget Seller

Their blog formatting and Amazon affiliate setup helped me start earning consistently through my content.
— Sarah Paterson, Affiliate Blogger (USA)

Fast-loading site, modern design, and complete Google service setup — all done smoothly.
— Hira Sheikh, Tech Blogger & Reviewer

I was confused between Shopify and WordPress, but they guided me perfectly and delivered a great online store!
— David Lee, Film Maker