The Evolution of the Internet Understanding Web 3.0
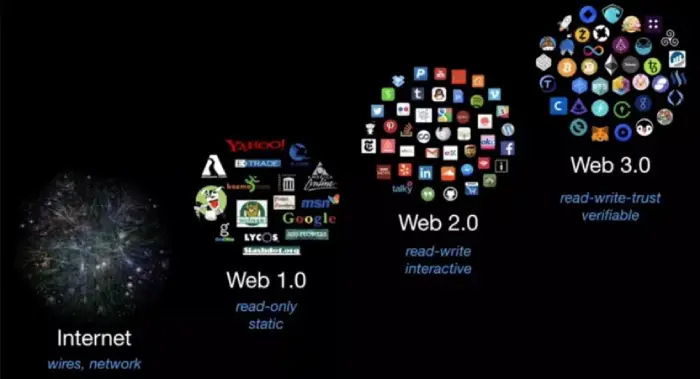
The internet has revolutionized how we connect, communicate, and access information. From its early days as a simple network to the dynamic Web 2.0 era, the internet has continually evolved. Now, we stand on the brink of Web 3.0, a new phase promising decentralization, enhanced user experiences, and greater control over data. This article explores the evolution of the internet, focusing on the emergence and implications of Web 3.0.
The Origins of the Internet
Since its inception, the Internet has undergone significant transformations, shaping the way we communicate, access information, and conduct business. From dial-up connections to Web 2.0, each phase brought new technologies and paradigms. Web 3.0 is on the horizon, poised to transform the internet in a new digital age. This article explores its evolution, concepts, technologies, and implications.
The Origins of the Internet
The Birth of the Internet
In the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense developed ARPANET to communicate during the Cold War, laying the foundation for the modern internet.
Read more about to choose and get my services.
Evolution of Internet Protocols
Internet protocols evolved from HTTP to TCP/IP, enabling faster and smoother communication and data exchange.
Introduction to Web 3.0
Defining Web 3.0
Web 3.0 focuses on decentralization, transparency, and user empowerment, offering a smarter, more personalized internet experience.
Characteristics of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 integrates AI, blockchain, and smart technologies to create adaptive, intelligent, and user-centric online experiences.
Key Features and Technologies of Web 3.0
Decentralization and Blockchain Technology
Decentralization puts power in the hands of users. Blockchain provides secure, transparent, and tamper-proof platforms for online interactions.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning personalize user experiences and optimize online operations.
Impacts of Web 3.0 on Industries and Society
Enhanced Data Privacy and Security Measures
Web 3.0 ensures robust data privacy and security, putting users in control of their digital data.
Transforming Business Models and User Experiences
Web 3.0 enables user-centric business models, personalized experiences, and innovative digital services.
Watch video content more about this topic.
Challenges and Considerations in the Adoption of Web 3.0
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles: Navigating new rules and regulations for decentralized systems is critical for smooth adoption.
Interoperability and Standardization Issues: Different platforms and smart contracts must work seamlessly together to avoid fragmentation.
Future Trends and Potential Developments in Web 3.0
Emerging Applications and Use Cases: Web 3.0 enables decentralized finance, NFTs, digital identity, and supply chain innovations.
Scalability and Performance Enhancements: Technologies like sharding, layer 2 solutions, and improved consensus algorithms ensure faster, more efficient systems.
Closing Thoughts
Future Trends and Potential Developments in Web 3.0
Web 3.0, with decentralization, AI, and privacy-focused innovations, offers a more secure, efficient, and inclusive digital world.
FAQs
What distinguishes Web 3.0 from previous iterations of the Internet?
Web 3.0 offers a more intelligent and personalized experience with decentralization via blockchain technology.
How does decentralization play a role in Web 3.0 technology?
Decentralization shifts power and control to users, enabling peer-to-peer transactions and promoting innovation in a more open ecosystem.
What challenges are organizations likely to face when adopting Web 3.0 principles?
Challenges include infrastructure upgrades, alignment with decentralized systems, and compliance with data privacy regulations.
What are some potential real-world applications of Web 3.0 in different industries?
Healthcare can use decentralized data sharing, finance can leverage blockchain for peer-to-peer transactions, and other sectors can innovate through secure, user-controlled systems.